IC designation
There are various coding systems (designations, markings)of IC,
operating both internationally and within individual countries or firms.
In European countries, the IC coding system is similar to that adopted
for encoding discrete semiconductor devices, and is used by firms producing
semiconductor devices, various countries (England, Belgium, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, Sweden,
France, Germany and others.). Basic principles of coding a system by which symbols are assigned
international organization Association International Pro Electron, are given below. The code consists of
three letters followed by a serial number, for example:

- Signal Conversion Principle:
S – digital;
Т – analog;
V – mixed (analog-to-digital and vice versa). - The second letter has no special meaning (selected by the manufacturer), with the exception of
the letter H, which denotes hybrid schemes. For digital circuits, the first two letters reflect them
technological features:
FY – emitter-coupled logic (ECL);
FD, GD – MOS logic;
FQ – diode-transistor logic (DTL);
GA – low-power TTL logic;
FL, GF – standard TTL logic;
GJ – high speed TTL logic;
GM – low-power TTL with Schottky;
НВ – CMOS logic 4000А series;
НС – CMOS logic 4500В series. - Operating temperature range, ° С:
А – temperature range not standardized;
В – from 0 to +70;
С – from -55 to +125;
D – from -25 to +70;
Е – from -25 to +85;
F – from -40 to +85;
G – from -55 to +85. - A serial number of four or more digits. If it consists of less than four digits, the number of digits increases to four by adding zeros in front of them.
- 6. Type of shell. May be indicated by one or two letters. With a two-letter designation
housing options the first letter reflects the design:
C - cylindrical body;
D - with two-row parallel arrangement of conclusions (DIP);
E - powerful with a two-row arrangement of conclusions (with an external heat sink);
F - flat (with a bilateral arrangement of conclusions);
G - flat (with a four-sided arrangement of conclusions);
K - case type TO-3;
M - multirow (more than four rows of conclusions);
Q - with four-row parallel arrangement of conclusions;
R - powerful with four-row arrangement of conclusions (with external heat sink);
S - with a single-row arrangement of conclusions;
T - with a three-row arrangement of conclusions.
The second letter indicates the body material:
G - glass ceramics;
M - metal;
P - plastic;
X - other.
Single letter case designations:
C - cylindrical;
D - ceramic;
F - flat;
L - tape crystal holder;
P - Plastic DIP;
Q - with a four-row arrangement of conclusions;
T - miniature plastic;
U - Unpacked IC.
Note. In the code, valid until 1973, the third letter indicated
on the functionality of the chip:
A - linear gain;
B - frequency conversion / demodulation;
C - oscillation generation;
N - logic circuits;
J - bistable or multistable circuits (frequency dividers, triggers, counters, registers);
K - monostable circuits (single vibrators);
L - digital level converters (decoders, drivers);
M - circuits with a complex logical configuration (for example, an adder);
N - two-stable or multi-stable circuits (with long-term storage of information);
Q - random access memory (RAM);
R - read only memory (ROM);
S - readout amplifier with digital output;
Y - other schemes.
A - linear gain;
B - frequency conversion / demodulation;
C - oscillation generation;
N - logic circuits;
J - bistable or multistable circuits (frequency dividers, triggers, counters, registers);
K - monostable circuits (single vibrators);
L - digital level converters (decoders, drivers);
M - circuits with a complex logical configuration (for example, an adder);
N - two-stable or multi-stable circuits (with long-term storage of information);
Q - random access memory (RAM);
R - read only memory (ROM);
S - readout amplifier with digital output;
Y - other schemes.
The first two digits following the letter designation means the serial
number (from 10 to 99), and the third digit is the range of operating temperatures, ° С:
0 - temperature range not standardized;
1 – from 0 to +70;
2 – from -55 to 125;
3 – from -10 to +85;
4 – from +15 to +55;
5 – from -25 to +70;
6 – from -40 to +85.
0 - temperature range not standardized;
1 – from 0 to +70;
2 – from -55 to 125;
3 – from -10 to +85;
4 – from +15 to +55;
5 – from -25 to +70;
6 – from -40 to +85.
However, the marking method described above is not standard.
Some chip manufacturers have their own way of labeling. Conventional designation
microcircuit consists of a prefix indicating the manufacturer or type of device, alphanumeric
designations of the type of microcircuit and suffix, specifying the modification of the device, operating conditions and
type of shell. Many firms, buying a license to manufacture a particular chip, or
they leave it with the previous symbol, or replace the prefix of the company that developed this chip,
on your own, therefore, uniquely determine the type of chip by its conditional, designation is quite
difficult. But, knowing the system of symbols of microchips of various companies, you can find an analogue of another
firms for the available and indirect way to obtain the necessary information.
It should be noted that the same letter prefixes can
belong to microchips of different manufacturers. Therefore, among other things, you must pay
attention to the manufacturer’s logo printed on the chip body. For example, microchips
firms International Rectifier, IR are marked as below:
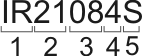
- Manufacturer's designation – IR (International Rectifier).
- Working voltage, В:
22 – 1200 V;
21 – 600 V;
20 – 150 V;
12 – 20 V;
11 – 5 V. - Serial number.
- Additional number characterizing manufacture details.
- Package type:
not specified – PDIP;
S – SOIC;
J – PLCC;
Q – MQFP;
SP – PSOP.
It should be borne in mind that the technical data on components, devices are in documents called Data Sheet.
Specific information on the practical application of components and devices can be found in documents called Application Notes.